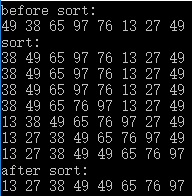
直接插入排序 类似于扑克牌抓牌,假设习惯是牌从左往右升序,那么抓到新的牌后,从右到左找牌,找到小等于抓到的牌的那张牌,则新抓的牌就应该插入到那张牌的后面。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std;void InsertionSort (vector<int >& vec) void Print (const vector<int >& vec) int main () vector<int > vec = { 49 , 38 , 65 , 97 , 76 , 13 , 27 , 49 }; cout << "before sort:" << endl; Print (vec); cout << "sort:" << endl; InsertionSort (vec); cout << "after sort:" << endl; Print (vec); } void InsertionSort (vector<int >& vec) int length = vec.size (); int preIndex; int currentValue; for ( int i = 1 ; i < length; i++ ) { preIndex = i - 1 ; currentValue = vec[i]; while ( preIndex >= 0 && currentValue < vec[preIndex] ) { vec[preIndex + 1 ] = vec[preIndex]; preIndex--; } vec[preIndex + 1 ] = currentValue; Print (vec); } } void Print (const vector<int >& vec) for ( int v : vec ) { cout << v << " " ; } cout << endl; }
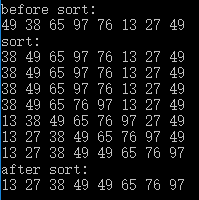
折半(二分)插入排序 跟直接插入排序的区别其实只有一处,就是在给当前数找位置的时候,因为已知前面的数字都已经有序,所以可以使用二分查找减少比较次数,速度比直接插入排序快。
因为找到插入位置后,需要将后续对应的数全部往后移动,移动次数不变,所以时间复杂度依旧为O(n^2)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 #include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std;void BinaryInsertionSort (vector<int >& vec) void Print (const vector<int >& vec) int main () vector<int > vec = { 49 , 38 , 65 , 97 , 76 , 13 , 27 , 49 }; cout << "before sort:" << endl; Print (vec); cout << "sort:" << endl; BinaryInsertionSort (vec); cout << "after sort:" << endl; Print (vec); } void BinaryInsertionSort (vector<int >& vec) int length = vec.size (); int left; int right; int mid; int currentValue; for ( int i = 1 ; i < length; i++ ) { left = 0 ; right = i - 1 ; currentValue = vec[i]; while ( left <= right ) { mid = ( left + right ) / 2 ; if ( currentValue < vec[mid] ) { right = mid - 1 ; } else { left = mid + 1 ; } } for ( int j = i - 1 ; j >= left; j-- ) { vec[j + 1 ] = vec[j]; } vec[left] = currentValue; Print (vec); } } void Print (const vector<int >& vec) for ( int v : vec ) { cout << v << " " ; } cout << endl; }